What is a Spray Dryer Used For?
Spray drying is a fascinating process that has become an indispensable part of various industries. But what exactly is a spray dryer used for? This article delves into the multifaceted applications of spray dryers, exploring how they transform liquid substances into dry powders and how this capability is harnessed across different sectors.
Understanding Spray Drying
Spray drying is a well-known method of particle production that involves the transformation of a fluid material into dried particles using a hot gaseous drying medium. Its first observation dates back to 1860, and a primitive spray dryer device was patented by Samuel Percy in the United States in 1872.
Since its discovery, the spray-drying technique has seen significant improvements in operational design and applications. Initially, the primary spray dryer devices were inefficient and posed safety risks. Once these issues were resolved, spray drying became an attractive method for the food industry, particularly for producing milk powder in the 1920s. This application remains one of the most important uses of spray drying today.
The evolution of spray drying was significantly influenced by World War II, which created an urgent need to reduce the weight and volume of food and other materials for transport. As a result, spray drying became a benchmark in the dairy products industry. In the post-war period, the method continued to progress, extending its reach to the pharmaceutical, chemical, ceramic, and polymer industries.
Even after more than a century of research, spray drying remains a target for innovation due to the increasing demand for complex particles with specific characteristics. It is considered a powerful technological process because it enables the production of free-flowing particles with well-defined sizes. The ability to use different feedstocks, coupled with high productivity and broad applications, makes spray drying increasingly attractive to the scientific community.
Spray drying is a method of producing a dry powder from a liquid or slurry by rapidly drying it with a hot gas. This process is prevalent in numerous industries due to its efficiency and ability to produce consistent, high-quality products. The liquid feedstock is atomized into fine droplets, which are then exposed to a hot drying medium, typically air. As the moisture evaporates, the solid particles form and are collected as a fine powder.
How Spray Dryers Work
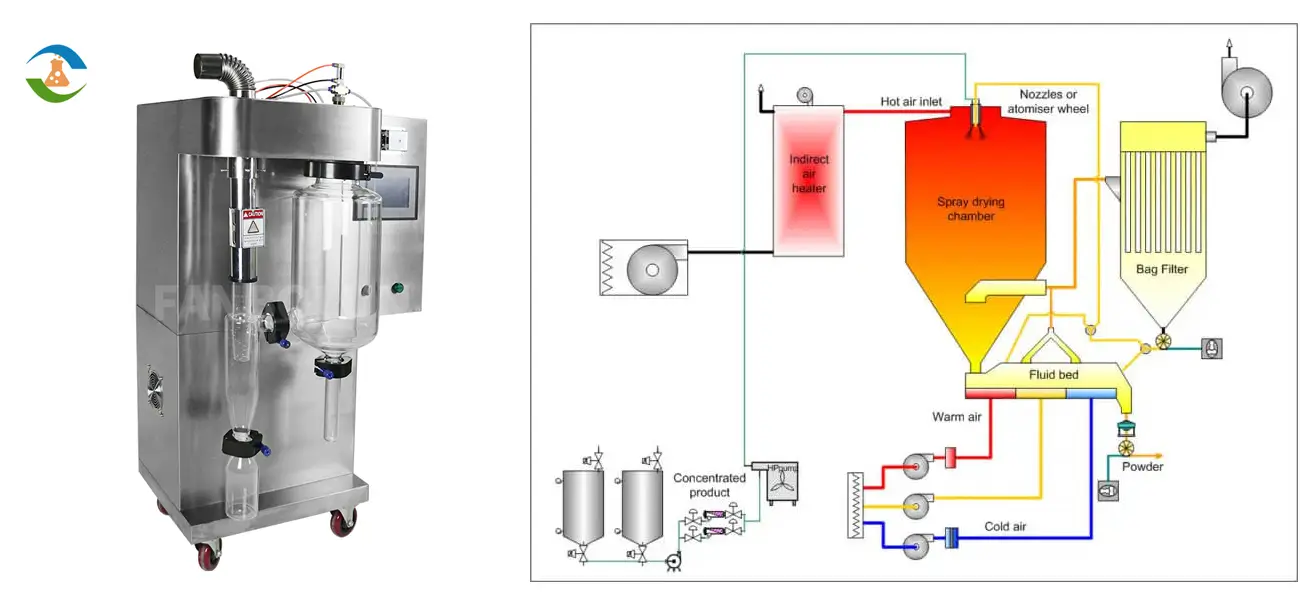
The spray drying process involves three main stages: atomization, drying, and powder recovery.
1. Atomization
Atomization is the process of breaking up the liquid feed into fine droplets. This is typically achieved using a nozzle or a rotary atomizer. The choice of atomizer depends on the properties of the liquid feed and the desired characteristics of the final powder. Fine droplets provide a large surface area for rapid drying, which is essential for producing a high-quality powder.
2. Drying
Once the liquid feed is atomized, the fine droplets are introduced into a hot drying medium, usually air. The drying medium is heated to a temperature that promotes rapid evaporation of the moisture content without degrading the product. The droplets are suspended in the hot air, and as they travel through the drying chamber, the moisture evaporates, leaving behind solid particles.
3. Powder Recovery
The final stage of spray drying is powder recovery. The dried particles are separated from the drying medium using a cyclone separator or a bag filter. These systems ensure that the fine powder is collected efficiently while preventing loss of product. The recovered powder is then subjected to further processing, such as milling or sieving, to achieve the desired particle size and distribution.
What are the critical factors to consider in spray drying?
Several factors influence the efficiency and outcome of spray drying. These include the properties of the feed liquid, such as viscosity and solids content, the atomization process, the temperature and flow rate of the drying medium, and the design of the spray dryer itself. Understanding and optimizing these factors is crucial for achieving the desired product quality.
Key Applications of Spray Dryers
1. Food and Beverage Industry
Spray drying is extensively used in the food and beverage industry. One of the most common applications is the production of milk powder. By removing the water content from liquid milk, spray dryers produce milk powder that is easier to store, transport, and has a longer shelf life. But did you know spray drying is also used to create coffee powders, flavorings, and even baby formula?
Spray dryers help preserve the nutritional content and flavor of the product while providing a convenient, stable form for consumers. The versatility of spray drying allows for the encapsulation of flavors and nutrients, ensuring that the end product meets the desired taste and quality standards.

2. Pharmaceutical Industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, spray drying plays a critical role in the formulation of medications. The process is used to produce fine powders that are easy to handle and have a high degree of uniformity. This is particularly important for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), where precise dosing is crucial.
Spray drying can enhance the solubility and bioavailability of drugs, making them more effective. It is also used in the production of inhalable medications, where the powder form needs to be extremely fine to be efficiently delivered to the lungs. Have you ever wondered how asthma inhalers deliver such fine particles? Spray drying is often the answer.

3. Chemical Industry
The chemical industry relies on spray dryers for producing various chemicals in powdered form. This includes catalysts, pigments, and detergents. Spray drying provides a controlled environment that ensures the consistency and quality of the final product. Additionally, it can handle heat-sensitive materials, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of certain chemical compounds.

4. Ceramic and Material Sciences
Spray dryers are also used in the production of ceramic powders. These powders are later formed into shapes and sintered to create ceramic components used in various applications, from household items to advanced technological devices. The ability to control particle size and moisture content makes spray drying an ideal method for producing high-quality ceramic materials.

5. Biotechnology
In biotechnology, spray drying is used to stabilize biological materials such as enzymes, proteins, and probiotics. The process helps maintain the activity and viability of these sensitive substances by rapidly drying them into a stable powder form. This is particularly useful for creating long-lasting, easily transportable products that can be rehydrated when needed.

Can spray drying be used for all types of liquids?
While spray drying is versatile, it is not suitable for all types of liquids. The process works best with liquids that can be atomized into fine droplets and have a consistent composition. Highly viscous or non-homogeneous liquids may require pre-treatment or alternative drying methods. However, advancements in spray drying technology continue to expand the range of applicable materials.
The Advantages of Spray Drying
Spray drying offers several advantages that make it a preferred method in many industries. Firstly, it provides excellent control over particle size and distribution, which is essential for achieving consistent product quality. The process is also highly efficient, capable of converting large volumes of liquid into dry powder in a relatively short time.
Moreover, spray drying is suitable for heat-sensitive materials. The rapid drying process minimizes exposure to high temperatures, preserving the integrity and functionality of the substances being dried. This is especially important in the food, pharmaceutical, and biotechnology industries, where the quality and efficacy of the product are paramount.



How does spray drying compare to other drying methods?
Spray drying is often compared to other drying methods, such as freeze drying and drum drying. Each method has its advantages and limitations. Spray drying is typically faster and more cost-effective for large-scale production, while freeze drying is better suited for preserving the quality of highly sensitive materials. Drum drying, on the other hand, is less expensive but may not offer the same level of control over particle size and quality.
Types of Spray Dryers
There are several types of spray dryers, each designed to meet specific needs and applications. The most common types include:
1. Rotary Atomizer Spray Dryers
Rotary atomizer spray dryers use a high-speed rotating disk to atomize the liquid feed. The centrifugal force generated by the rotating disk breaks up the liquid into fine droplets. This type of spray dryer is ideal for handling large volumes of liquid feed and producing powders with a narrow particle size distribution.
2. Nozzle Atomizer Spray Dryers
Nozzle atomizer spray dryers use a nozzle to atomize the liquid feed. There are two main types of nozzles: pressure nozzles and pneumatic nozzles. Pressure nozzles use high-pressure liquid feed to create fine droplets, while pneumatic nozzles use compressed air to atomize the liquid. Nozzle atomizers are suitable for producing fine powders and handling viscous liquids.
3. Fluidized Spray Dryers
Fluidized spray dryers combine spray drying and fluidized bed drying. In this type of dryer, the fine droplets are introduced into a fluidized bed of pre-dried powder. The fluidized bed provides additional drying and cooling, resulting in a more uniform and consistent product. Fluidized spray dryers are commonly used for heat-sensitive materials and products that require precise control over moisture content.
4. Closed-Cycle Spray Dryers
Closed-cycle spray dryers are designed to handle hazardous or sensitive materials. In a closed-cycle system, the drying medium is recycled and reused, minimizing the risk of contamination and exposure to the environment. This type of spray dryer is often used in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries where safety and product purity are paramount.
Conclusion
Spray drying is a powerful and versatile process used in a wide range of industries. From food and pharmaceuticals to chemicals and ceramics, it provides an efficient way to convert liquids into high-quality powders. The ability to control particle size, preserve sensitive materials, and produce consistent products makes spray drying an invaluable tool in modern manufacturing.
Whether creating instant coffee, life-saving medications, or advanced ceramic materials, spray dryers continue to play a crucial role in shaping our world. Understanding the history, working principles, and types of spray dryers helps appreciate their significance and the technological advancements that drive their continuous evolution. As technology advances, the applications of spray drying are likely to expand further, promising even greater innovations and applications in the future.
What Are the Benefits of Spray Drying?
Spray drying is a fast, cost-effective method that turns liquids into powder. It preserves nutrients, extends shelf life, enhances consistency, and is widely ...
What is a Spray Dryer Used for in a Laboratory?
A spray dryer in a laboratory converts liquid solutions into dry powders. It’s essential for producing consistent, stable, and high-quality powders for pharma...
What is Spray Drying?
Spray drying is a process that transforms liquid or slurry into dry powder. It involves rapidly evaporating moisture with hot gas, producing fine, uniform par...